Innovations in Automotive Safety Features
The automotive industry continually evolves, placing a significant emphasis on enhancing safety for drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. Modern vehicles integrate a complex array of technologies and design principles aimed at preventing accidents and mitigating their impact when they do occur. These advancements range from sophisticated sensor systems that monitor surroundings to structural improvements that absorb collision forces, all contributing to a safer transportation experience across various driving conditions and environments.
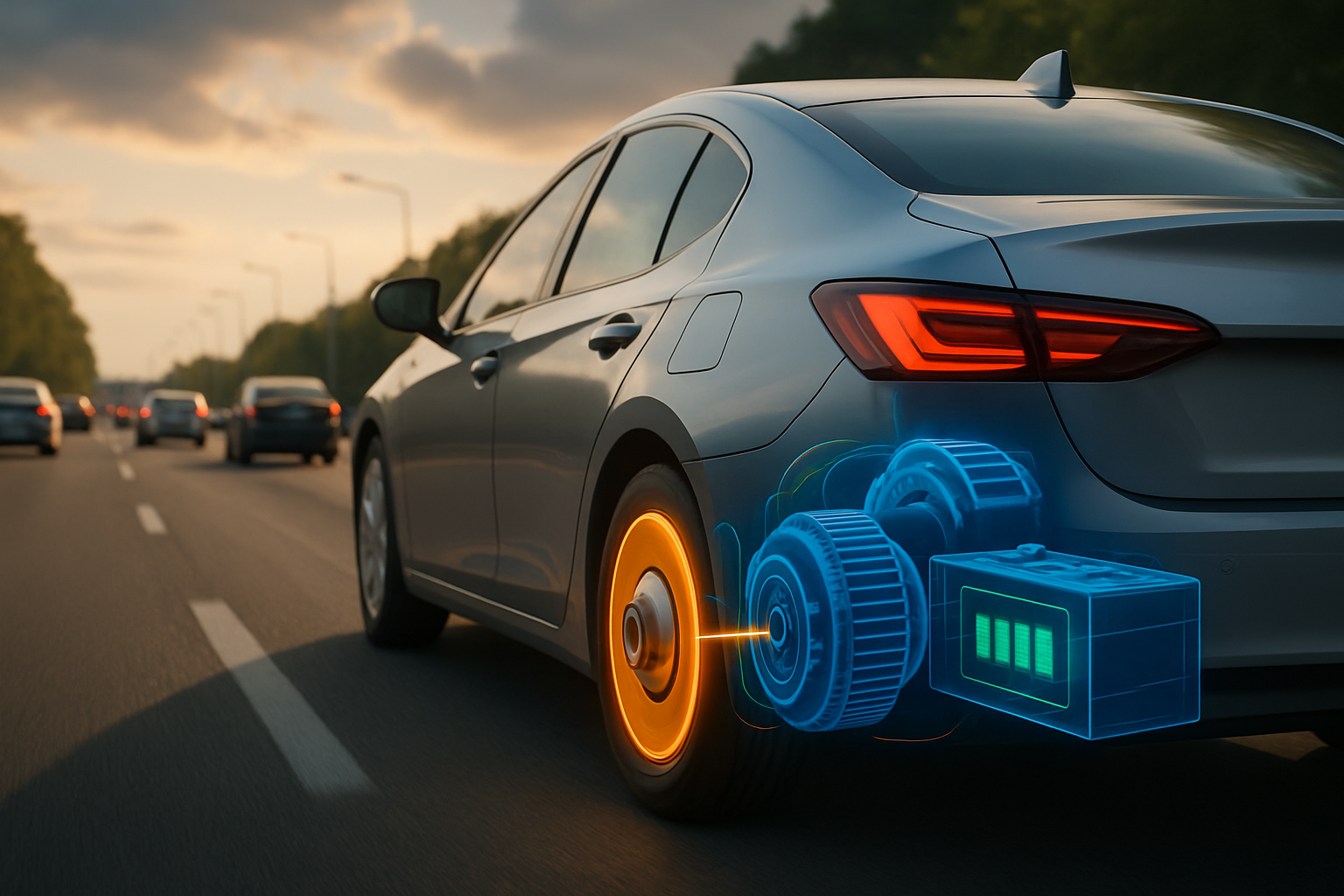

How Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Enhance Driving Safety?
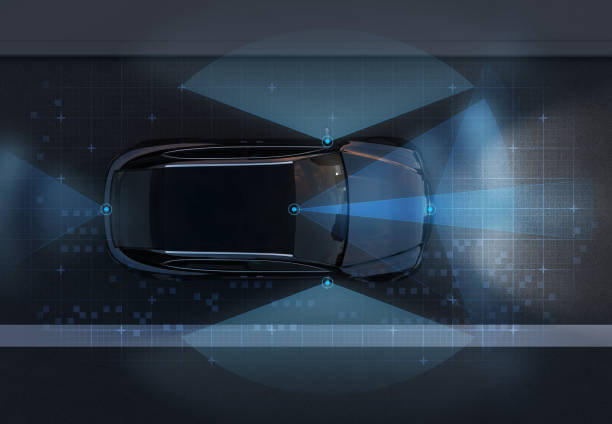
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) represent a pivotal area of innovation in automotive safety, actively working to prevent collisions and support drivers. These systems utilize a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and lidar to perceive the vehicle’s surroundings and react to potential hazards. Common ADAS features include Adaptive Cruise Control, which maintains a set distance from the vehicle ahead, and Lane-Keeping Assist, designed to help keep the car centered in its lane. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) can detect imminent collisions and apply the brakes if the driver does not respond in time, significantly reducing impact severity or avoiding the crash altogether.
Blind-spot monitoring systems alert drivers to vehicles in their blind spots, while rear cross-traffic alerts warn of approaching traffic when backing out of a parking space. These technologies enhance overall driving awareness and reduce the cognitive load on the driver, contributing to safer journeys. The continuous development of ADAS technology aims to make driving more intuitive and less prone to human error, supporting greater road safety.
What Role Does Vehicle Design Play in Automotive Protection?
Beyond electronic systems, the physical design and engineering of a vehicle are fundamental to occupant protection. Vehicle structures are meticulously engineered with crumple zones, which are areas designed to deform and absorb kinetic energy during an impact, diverting forces away from the passenger compartment. The use of high-strength steel and advanced alloys in the chassis creates a rigid safety cell around occupants, maintaining structural integrity in a crash.
Interior design elements also play a crucial role. Multiple airbags, strategically placed throughout the cabin (front, side, curtain, knee), deploy rapidly to cushion occupants during a collision. Seatbelt pretensioners tighten belts instantaneously upon impact, holding occupants securely in place, while load limiters reduce the force exerted on the body. Headrests are designed to mitigate whiplash injuries by supporting the head and neck. These passive safety features are critical for mitigating injury severity when an accident occurs, complementing the preventative measures of active safety systems.
Exploring Innovations in Active and Passive Safety Technology
Automotive safety technology can be broadly categorized into active and passive systems. Active safety features are designed to prevent accidents from happening. Examples include Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), which prevent wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. Electronic Stability Control (ESC) detects and reduces loss of traction, helping the driver maintain control during extreme steering maneuvers. Traction control systems prevent wheel spin during acceleration, especially on slippery surfaces.
Passive safety features, on the other hand, are designed to protect occupants during and immediately after a crash. Innovations in this area include advanced airbag designs that adapt inflation force based on impact severity and occupant size, as well as seatbelt reminders and post-collision braking systems that prevent secondary impacts. Newer integrated safety systems combine both active and passive elements, such as pedestrian detection systems that can initiate braking and prepare airbags for deployment simultaneously, offering a comprehensive approach to protection.
The Impact of Electric Vehicles on Safety Performance
Electric vehicles (EVs) introduce unique considerations and advantages regarding safety. The heavy battery packs typically located in the floor of an EV contribute to a lower center of gravity, which can enhance stability and reduce the risk of rollovers. The absence of a large engine block in the front allows for greater design flexibility in creating larger crumple zones and improved front-impact absorption structures. Many EVs are designed from the ground up as electric platforms, allowing engineers to integrate safety features optimally.
However, EVs also present specific safety aspects, such as the high-voltage battery system. Manufacturers implement robust protective casings and sophisticated thermal management systems to prevent battery damage and thermal runaway in the event of a crash. Additionally, the quiet operation of EVs at low speeds has led to the development of Acoustic Vehicle Alerting Systems (AVAS) or similar pedestrian warning systems, which emit sounds to alert pedestrians and cyclists to the vehicle’s presence, addressing a unique aspect of urban mobility safety.
Future Trends in Automotive Safety and Mobility
The trajectory of automotive safety is moving towards increasingly integrated and predictive systems, with the ultimate goal of achieving zero accidents. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication is a significant emerging trend, allowing vehicles to communicate with each other (V2V), with infrastructure (V2I), with pedestrians (V2P), and with the network (V2N). This interconnectedness enables real-time sharing of information about road conditions, traffic hazards, and emergency situations, providing advance warnings that can prevent accidents.
Further advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing the capabilities of ADAS, enabling more sophisticated decision-making and predictive accident avoidance. The development of higher levels of autonomous driving also promises to revolutionize safety by removing human error from the driving equation. While full autonomy presents complex challenges, its potential to drastically reduce collisions is a driving force behind ongoing research and development in the field of mobility and transport safety. These future innovations are set to redefine the standards of vehicle protection and occupant well-being.
Modern automotive safety features represent a continuous evolution of engineering and technology, combining proactive accident prevention with robust passive protection. From advanced driver-assistance systems that monitor surroundings to structural designs that absorb impact forces, and the specialized considerations of electric vehicles, the commitment to enhancing safety is unwavering. The ongoing integration of smart technologies and future mobility solutions aims to create an increasingly secure environment for all road users, reflecting a comprehensive approach to safeguarding journeys.