Blockchain's Legal Frontier: Smart Contracts and the Law
Introduction: In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital transactions, smart contracts are emerging as a revolutionary force, challenging traditional legal frameworks and offering new possibilities for automated, self-executing agreements. This article delves into the intricate world of smart contracts, exploring their legal implications and the hurdles they face in gaining widespread acceptance within existing legal systems.
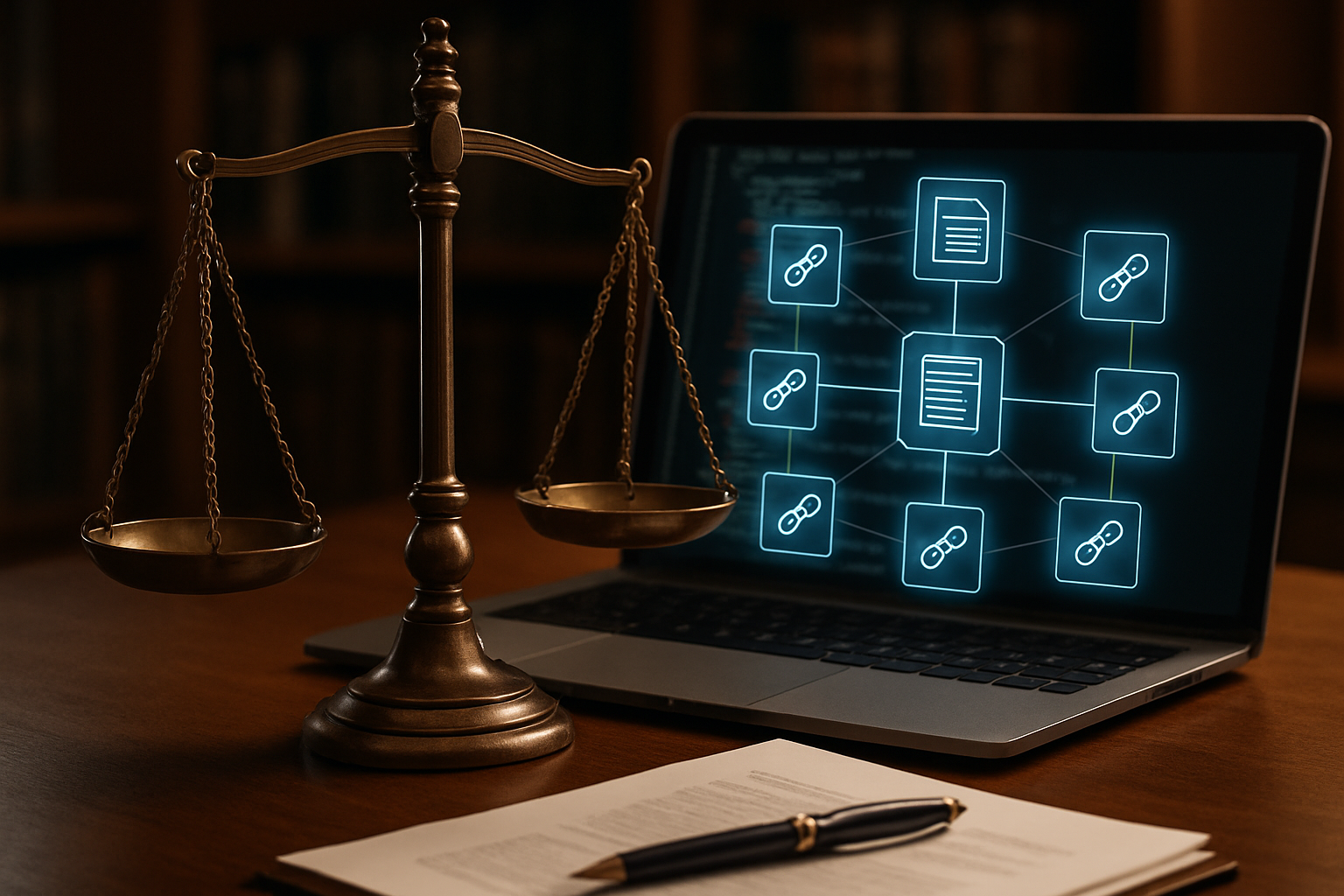

Legal Status and Recognition
The legal status of smart contracts remains a complex and evolving issue. While some jurisdictions have taken steps to recognize smart contracts as legally binding, others are still grappling with how to integrate them into existing legal frameworks. In the United States, states like Arizona, Nevada, and Tennessee have passed legislation explicitly recognizing smart contracts, but federal recognition remains limited. The European Union, through its blockchain strategy, is also exploring ways to incorporate smart contracts into its legal system.
Challenges in Contract Law
Smart contracts pose unique challenges to traditional contract law. One of the primary issues is the immutability of blockchain-based smart contracts, which conflicts with the legal principle of contract modification. Additionally, the code-based nature of smart contracts raises questions about interpretation and intent, as traditional legal concepts like offer, acceptance, and consideration may not directly translate to the digital realm. Courts and legal professionals are now faced with the task of bridging the gap between code and legal language.
Enforcement and Dispute Resolution
The self-executing nature of smart contracts presents both opportunities and challenges for enforcement and dispute resolution. While smart contracts can potentially reduce the need for litigation by automating contract execution, they also raise questions about how disputes can be resolved when things go wrong. Traditional legal remedies may be difficult to apply to decentralized, autonomous contracts. This has led to the development of new dispute resolution mechanisms, such as blockchain-based arbitration systems, which aim to provide quick and cost-effective solutions tailored to the digital age.
Privacy and Data Protection Concerns
As smart contracts often involve the storage and processing of personal data on blockchain networks, they raise significant privacy and data protection concerns. The immutable nature of blockchain conflicts with data protection principles like the right to be forgotten, enshrined in regulations such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Legal experts and technologists are working to develop solutions that balance the benefits of smart contracts with the need to protect individual privacy rights.
Regulatory Challenges and Adaptation
Regulators worldwide are struggling to keep pace with the rapid development of smart contract technology. The decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain networks challenges traditional regulatory approaches based on jurisdiction and centralized control. Some countries, like Malta and Switzerland, have taken proactive steps to create regulatory frameworks that accommodate blockchain technology and smart contracts. However, achieving a global consensus on regulation remains a significant challenge, as different jurisdictions approach the technology with varying levels of acceptance and caution.
The Future of Smart Contracts in Legal Practice
As smart contracts continue to evolve, they are likely to have a profound impact on legal practice. Legal professionals are increasingly required to understand coding and blockchain technology to effectively draft and interpret smart contracts. Law firms and legal education institutions are beginning to incorporate blockchain and smart contract courses into their curricula, preparing the next generation of lawyers for a digitally transformed legal landscape. The integration of artificial intelligence with smart contracts is also on the horizon, promising even more sophisticated and adaptive legal agreements.
In conclusion, smart contracts represent a significant leap forward in the digitization of legal agreements, offering potential benefits in efficiency, transparency, and cost reduction. However, their integration into existing legal systems poses numerous challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. As the technology matures and legal frameworks adapt, smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize how we conceive, execute, and enforce agreements in the digital age. The ongoing dialogue between technologists, legal experts, and policymakers will be crucial in shaping a future where smart contracts can coexist harmoniously with traditional legal principles, ensuring both innovation and legal certainty in the digital economy.