Biofeedback in Sports: Optimizing Performance Through Mind-Body Connection
In the realm of athletic excellence, a groundbreaking approach is reshaping how athletes train and compete. Biofeedback, a technique that allows individuals to gain awareness and control over their physiological processes, is emerging as a game-changer in sports performance optimization. This innovative method bridges the gap between mind and body, offering athletes unprecedented insights into their physical and mental states during training and competition.

The Foundations of Biofeedback in Sports
Biofeedback is rooted in the principle that individuals can learn to modulate their physiological processes through conscious control. In a sports context, this translates to athletes gaining the ability to regulate heart rate, muscle tension, brainwave activity, and other bodily functions that directly impact performance. The origins of biofeedback can be traced back to the 1960s, when researchers began exploring the potential of using electronic instruments to provide real-time information about bodily processes.
The application of biofeedback in sports gained traction in the 1970s and 1980s, with early adopters in disciplines such as archery and shooting, where precise control over physiological arousal is crucial. As technology advanced, so did the sophistication and accessibility of biofeedback devices, leading to broader adoption across various sports.
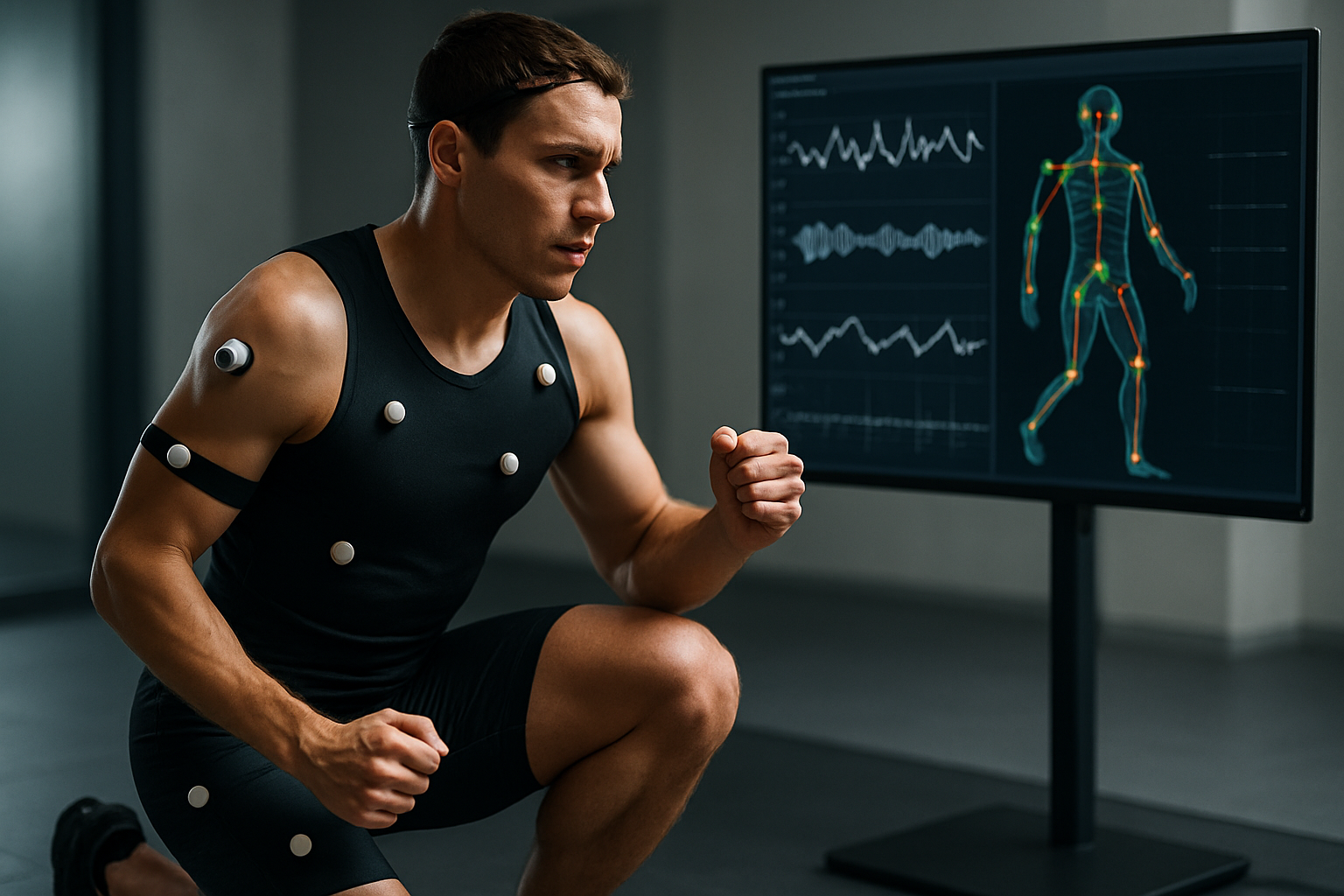
Today, biofeedback encompasses a range of modalities, including heart rate variability (HRV) training, neurofeedback, and electromyography (EMG) feedback. Each of these approaches offers unique insights into different aspects of an athlete’s physiological and mental state, allowing for targeted interventions and personalized training protocols.
The Science Behind Biofeedback in Athletic Performance
At its core, biofeedback in sports leverages the principle of operant conditioning, where desired behaviors are reinforced through immediate feedback. When athletes receive real-time information about their physiological states, they can learn to associate certain internal sensations with optimal performance conditions. This process of self-regulation becomes increasingly automated with practice, allowing athletes to maintain ideal psychological and physiological states even under intense competitive pressure.
Research has shown that biofeedback can lead to significant improvements in various aspects of athletic performance. For instance, studies on HRV biofeedback have demonstrated its efficacy in enhancing recovery, reducing performance anxiety, and improving overall stress management among athletes. Neurofeedback, which focuses on brainwave activity, has been linked to improvements in attention, focus, and mental resilience—critical factors in sports that demand high levels of concentration and emotional control.
Moreover, the integration of biofeedback with traditional training methods has been shown to accelerate skill acquisition and enhance motor learning. By providing immediate feedback on muscle activation patterns and movement efficiency, EMG biofeedback allows athletes to refine their technique with greater precision than relying on subjective feedback alone.
Practical Applications Across Sports Disciplines
The versatility of biofeedback makes it applicable to a wide range of sports, each benefiting from tailored approaches to performance enhancement. In endurance sports like long-distance running and cycling, HRV biofeedback can help athletes optimize their pacing strategies and improve their aerobic efficiency. By learning to maintain an ideal balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system activity, endurance athletes can push their limits while minimizing the risk of overtraining.
In precision sports such as golf and archery, neurofeedback has proven particularly valuable. By training athletes to achieve and maintain specific brainwave patterns associated with focus and calmness, these techniques can help improve shot accuracy and consistency. Golfers, for example, can learn to enter a state of relaxed concentration before each swing, potentially reducing the impact of performance anxiety on their game.
Team sports athletes are also finding value in biofeedback training. Football players, for instance, can use EMG feedback to refine their kicking technique, optimizing muscle recruitment patterns for more powerful and accurate shots. Basketball players might employ HRV training to enhance their recovery between high-intensity game periods, maintaining peak performance throughout the match.
Combat sports and martial arts practitioners benefit from biofeedback’s ability to enhance mind-body awareness and emotional regulation. By learning to control their physiological arousal levels, fighters can maintain composure under pressure, make better tactical decisions, and optimize their energy expenditure during bouts.
Implementing Biofeedback in Training Regimens
Integrating biofeedback into existing training programs requires a strategic approach and often involves collaboration between coaches, athletes, and sports psychologists. The process typically begins with an assessment phase, where baseline measurements are taken to identify areas for improvement. This might involve analyzing an athlete’s HRV patterns, brainwave activity during different performance states, or muscle activation sequences during specific movements.
Based on these assessments, personalized biofeedback training protocols are developed. These protocols often involve a combination of in-session training with specialized equipment and portable devices for ongoing practice. For instance, an athlete might undergo neurofeedback sessions with a sports psychologist to train specific brainwave patterns associated with peak performance. They would then use portable EEG devices to practice maintaining these optimal brain states during their regular training sessions.
Consistency is key in biofeedback training, with most protocols requiring regular practice over several weeks or months to see significant improvements. Athletes are typically encouraged to integrate biofeedback techniques into their pre-performance routines, using the skills they’ve developed to achieve optimal mental and physiological states before and during competition.
It’s important to note that biofeedback should complement, not replace, traditional training methods. The most effective approaches integrate biofeedback seamlessly with physical conditioning, technical skill development, and tactical training. This holistic approach ensures that improvements in physiological control translate directly to enhanced performance in the competitive arena.
Challenges and Considerations in Biofeedback Implementation
While the potential benefits of biofeedback in sports are substantial, its implementation is not without challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the need for specialized equipment and expertise to administer and interpret biofeedback data effectively. This can make biofeedback training inaccessible for some athletes and teams, particularly at lower competitive levels or in resource-constrained environments.
There’s also the question of individual variability in response to biofeedback training. Not all athletes will experience the same degree of benefit from these techniques, and it may take time to identify the most effective modalities for each individual. This underscores the importance of a personalized approach and the need for patience in the implementation process.
Privacy and ethical considerations come into play as well, particularly as biofeedback devices become more sophisticated and data-driven. The collection and use of physiological data raise questions about data ownership, athlete privacy, and the potential for misuse of this information in high-stakes competitive environments.
Furthermore, there’s a risk of over-reliance on technology, potentially leading athletes to become too dependent on external feedback rather than developing their internal awareness. Balancing the use of biofeedback tools with the cultivation of intuitive self-regulation skills is crucial for long-term performance benefits.
The Future of Biofeedback in Sports
As technology continues to advance, the future of biofeedback in sports looks increasingly promising. Emerging trends point towards more integrated, real-time feedback systems that can provide athletes with instant insights during training and competition. Wearable devices are becoming smaller, more accurate, and less intrusive, allowing for continuous monitoring without impeding performance.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are being developed to analyze vast amounts of biofeedback data, identifying patterns and offering personalized recommendations for performance optimization. This could lead to highly tailored training programs that adapt in real-time to an athlete’s physiological and psychological state.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are also being explored as platforms for immersive biofeedback training. These technologies could allow athletes to practice self-regulation skills in simulated competitive environments, bridging the gap between training and real-world performance.
The integration of biofeedback with other emerging fields, such as genetics and epigenetics, may lead to even more personalized approaches to performance enhancement. By understanding how an individual’s genetic makeup influences their response to different types of biofeedback training, coaches and athletes could develop hyper-targeted interventions for maximum effect.
Ethical Implications and Regulatory Considerations
As biofeedback technologies become more sophisticated and widely adopted in sports, they raise important ethical questions that the sporting community must address. The line between performance enhancement and unfair advantage is often blurry, and the use of advanced biofeedback techniques may challenge existing notions of fair play and natural athletic ability.
Sports governing bodies will need to grapple with how to regulate the use of biofeedback technologies in competition. Should there be limits on the types of devices allowed during events? How can officials ensure that all athletes have equal access to these performance-enhancing tools? These are complex questions that will require careful consideration and ongoing dialogue within the sports community.
There are also concerns about the potential for biofeedback data to be used for purposes beyond performance enhancement. For instance, could physiological data be used to make decisions about player contracts or team selections? How can athletes’ privacy rights be protected in an era of increasingly invasive monitoring?
As the field evolves, it will be crucial to develop ethical guidelines and best practices for the use of biofeedback in sports. This may involve collaboration between sports organizations, technology developers, ethicists, and athletes themselves to create frameworks that balance the benefits of these technologies with the need to maintain the integrity and spirit of sport.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Biofeedback Training
Numerous athletes across various sports have reported significant performance improvements through the integration of biofeedback training into their regimens. While individual experiences vary, these case studies provide compelling evidence for the potential of biofeedback in sports performance enhancement.
One notable example comes from the world of professional tennis. A top-ranked player struggling with performance anxiety under high-pressure situations underwent a comprehensive HRV biofeedback training program. Over six months, the athlete learned to regulate their autonomic nervous system response during matches, resulting in improved composure in critical moments and a marked increase in their win percentage in tie-break situations.
In the realm of Olympic shooting, a marksman utilized neurofeedback to enhance their focus and emotional regulation. By training to achieve specific brainwave patterns associated with calm alertness, the athlete reported improved shot accuracy and consistency, particularly in high-stakes competition environments. This translated to a significant improvement in their competition scores and ultimately contributed to a medal-winning performance.
A professional basketball team incorporated biofeedback into their recovery protocols, using HRV monitoring to optimize training intensity and rest periods for individual players. This personalized approach led to a reduction in overtraining incidents, improved overall team fitness, and a notable decrease in injury rates over the course of a season.
These success stories, while anecdotal, highlight the diverse applications of biofeedback across different sports and its potential to address various aspects of athletic performance, from mental preparation to physical recovery and injury prevention.
Integrating Biofeedback with Traditional Coaching Methods
For biofeedback to reach its full potential in sports, it must be effectively integrated with traditional coaching methods and training philosophies. This integration requires a shift in mindset for many coaches and athletes, moving towards a more data-driven, individualized approach to performance enhancement.
Coaches play a crucial role in this integration process. They need to be educated about the principles of biofeedback, its potential benefits, and how to interpret and apply the data it provides. This may involve collaboration with sports psychologists and biofeedback specialists to develop comprehensive training programs that incorporate both physiological and psychological elements.
The most successful implementations of biofeedback in sports often involve a team approach, where coaches, athletes, sports scientists, and medical staff work together to analyze data, set goals, and track progress. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that biofeedback insights are contextualized within the broader framework of an athlete’s training and development.
It’s important to recognize that biofeedback should not be seen as a replacement for traditional coaching wisdom or the invaluable experience of seasoned athletes. Instead, it should be viewed as a complementary tool that can provide objective data to support and refine existing training methods. The art of coaching lies in balancing these technological insights with the human elements of motivation, strategy, and interpersonal dynamics.
The Transformative Potential of Biofeedback in Sports
As we look to the future of athletic performance, biofeedback stands out as a transformative technology with the potential to redefine the boundaries of human achievement in sports. By bridging the gap between mind and body, these techniques offer athletes unprecedented control over their physiological and psychological states, paving the way for new levels of performance optimization.
The integration of biofeedback in sports training represents more than just a technological advancement; it signifies a shift towards a more holistic, personalized approach to athletic development. As these technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, they have the potential to democratize high-level performance training, allowing athletes at all levels to benefit from insights once reserved for elite competitors.
However, as with any powerful tool, the responsible and ethical implementation of biofeedback in sports will be crucial. The sporting community must navigate the challenges of privacy, fairness, and the preservation of the fundamental human elements that make sports so compelling.
Ultimately, the true value of biofeedback in sports lies not just in its ability to enhance performance, but in its potential to deepen our understanding of human physiology and psychology under the extreme conditions of athletic competition. As we continue to explore and refine these techniques, we may not only push the boundaries of athletic achievement but also gain valuable insights into the remarkable capabilities of the human mind and body.